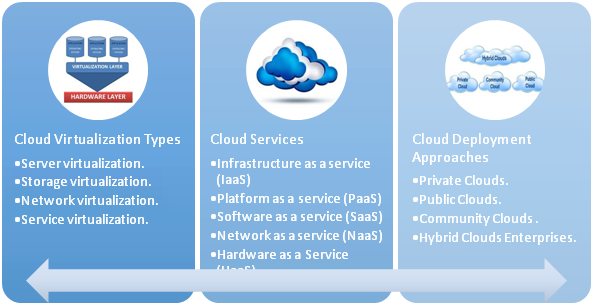
Many-to-one virtualization enables the creation of virtual or logical resources from multiple physical resources. This is the core context of cloud computing in which multiple physical resources are grouped together to form one cloud. Virtualization refers to OS virtualization as administrators can implement it by VMware, Xen, or other hypervisor-based technologies. Virtualization is not cloud, rather an enabler for establishing and managing clouds. In the Cisco cloud concept, virtualization is extended to incorporate various types of virtualization, such as network, computer, storage, and services. Generally, there are five varieties of cloud services and four types of deployment approaches, Figure 1.1 illustrates these concepts.
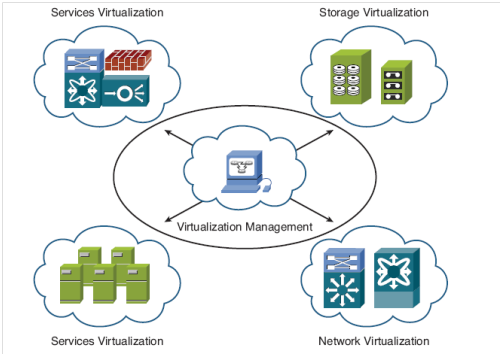
Virtualization is useful for several purposes such as sharing a computer system among multiple users, isolating users from each other, and emulating hardware on another machine. Figure 1.2 illustrates the virtualization types.
Server virtualization
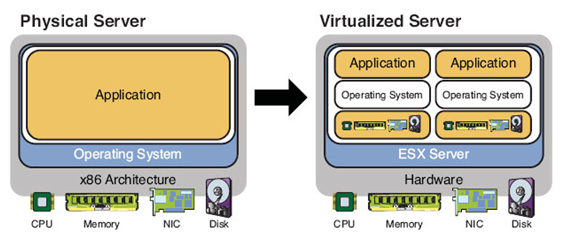
Hardware virtualization or server virtualization is the best known application for hardware virtualization. Server virtualization changes the rules by breaking the traditional model of one physical server playing host to a single operating system by creating several virtual machines on top of a single server using hypervisor technology. Computer hardware was designed to run a single operating system and a single application, this leaves most machines vastly underutilized. Virtualization lets the users run multiple virtual machines on a single physical machine, sharing the resources of that single computer across multiple environments. Figure 1.3 illustrates the differences between the physical server and the virtual server.
In a traditional server model, there is a single OS image for each machine, software and hard ware are tightly coupled, multiple applications often conflict, and there is a single IP address for each server. In virtualization, there is a separation of OS and hardware, OS and application contained in a single virtual machine (VM), applications are isolated from one another, hardware independence, and virtual IP address for each VM. Following are the advantages of server virtualization:
- Partitioning
- Single physical machine can run multiple operating systems on it.
- Divide the physical system resources among virtual machines.
- Each VM work independent and does not know the presence of the other.
- Management
- Failure of one VM does not affect other VMs.
- Each VM could be management separately and there is individual performance for each VM.
- Encapsulation
- The state of any VM can be saved in a file.
- Easy moving and copying VM files information.
- Flexibility
- Allows provisioning and migration of any VM to a similar machine on any physical server.
- Usage of multiple OS platforms, for example, Windows, Linux.
- Allows VM configuration changes without actually bringing the VM down.
Storage virtualization
Storage virtualization refers to providing a logical, abstracted view of physical storage devices. It provides a way for many users or applications to access storage without being concerned with where or how that storage is physically located or managed. Storage systems may use virtualization concepts as a tool to enable better functionality and more advanced features within and across storage systems. Storage virtualization enables physical storage to be shared across multiple application servers. Physical devices behind the virtualization layer can be viewed and managed as if they are one large storage pool with no physical boundaries. The storage virtualization makes multiple separate storage devices appear as one device
Virtualization hides the complex process of where the data needs to be stored and bringing it back and presenting it to the user when it is required. Storage Area Network (SAN) arrays use this concept of storage virtualization. SANs enables scalable and flexible storage resource allocation, efficient backup solutions, and higher storage utilization. Storage virtualization provides the following benefits:
- Resource optimization.
- Cost of operation.
- Increased availability.
- Improved performance.
- Simpler data migration and mobility.
- Development of a service catalog.
- Ability to monitor capacity utilization and performance.
- Signification cost savings.
Network virtualization
Network virtualization is the process of combining hardware and software network resources and network functionality into a single software based administrative entity for virtual network, or mapping two or more disparate networks into a single network. This concept enables the deployment of different architectures and protocols over a shared physical infrastructure and makes it look as if all remote networks are in a single place. The goal of network virtualization is to provide systems and users with efficient, controlled, and secure sharing of the networking resources. Network virtualization involves platform virtualization, often combined with resource virtualization, and it is true that the final product of network virtualization is the virtual network.
Virtual networks are classified into two broad types, external and internal. External virtual networks consist of several local networks that are administered by software as a single unit. The main components of classic external virtual networks are switch hardware and VLAN software technology. Examples of external virtual networks include large corporate networks and data centers. The internal virtual network consists of one system using virtual machines or zones that are configured over at least one pseudo network interface. These containers can communicate with each other as though on the same local network, providing a virtual network on a single host. The building blocks of the virtual network are Virtual Network Interface Cards or Virtual NICs (VNICs) and virtual switches.
Components of a virtual network
- Network hardware, such as switches and network interface cards (NICs).
- Network elements such as firewalls and load balancers.
- Networks, such as virtual LANs (VLANs) and containers such as virtual machines.
- Network storage devices.
- Network M2M elements such as telecommunications 4G HLR and SLR devices.
- Network mobile elements such as laptops, tablets, and cell phones.
- Network media, such as Ethernet and Fiber Channel.
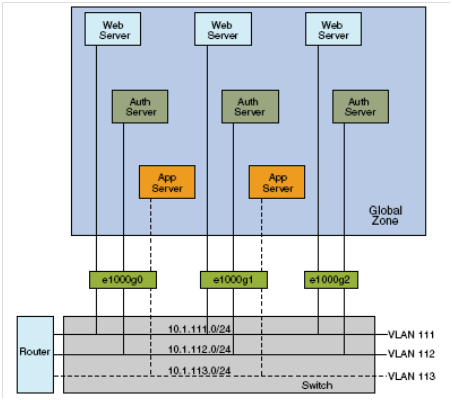
It is possible to configure multiple virtual networks within a single network unit, for example a switch using VLANs. Figure 1.4 illustrates a system with three physical NICs without VLANs, the user would configure different systems to perform specific functions and connect these systems to separate networks. For example, Web servers would be connected to one LAN, authentication servers to another, and application servers to a third network. With VLANs and zones, the user can collapse all eight systems and configure them as zones in a single system. Hence, uses VLAN tags, or VLAN IDs to assign a VLAN to each set of zones that performs the same functions.
Service virtualization
In the cloud world where almost everything is a service, the thinking of cloud computing as the transformation of computing that brings together service orientation with distributed manageability combined with the economies of scale from virtualization is imminent. Service virtualization is a fundamental mechanism for delivering services. Service virtualization in data centers refers to the services such as firewall services for additional security or load-balancing services for additional performance and reliability. Service virtualization is considered as a method to emulate the behavior of specific components in heterogeneous component based applications such as service oriented architectures.
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a software design and software architecture design pattern based on structured collections of discrete software modules, known as services that collectively provide the complete functionality of large software application. SOA allow easy cooperation of a large number of computers that are connected over a network. Every computer can run an arbitrary number of programs which is called services in a context that are built in a way to exchange information with any other service. Within the reach of the network without human interaction and without the need to make changes to the underlying program itself.
The virtual interface, often referred to as a Virtual IP (VIP), is exposed to the outside world, representing itself as the actual Web server, and manages the connections to and from the Web server as needed. This enables the load balancer to manage multiple Web servers or applications as a single instance, providing a more secure and robust topology than one allowing users direct access to individual Web servers. This is a one-to-many virtualization representation. One server is presented to the world, hiding the availability of multiple servers behind a reverse proxy appliance.
OneHoster is one of the best web hosting companies in Egypt, we offer many web hosting packages in Egypt and middle east like, cPanel storage hosting packages, cloud hosting, domain registration, dedicated servers solution, Email hosting, WordPress hosting, web hosting upgrades and hosting renewals to suit your requirements to host your website for small and medium sized businesses. OneHoster is also one of the top 10 website design companies, and top 10 digital marketing companies in Egypt and Middle east.
“OneHoster’s Team”